
The contraceptive implant is a highly effective form of birth control that is gaining popularity among women and people assigned female at birth. In fact, according to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the use of contraceptive implants has increased by 30% in the past decade.
But what exactly are contraceptive implants, and how do they work? In this guide, we will explore what you should know about contraceptive implants, including benefits, risks, and important questions you should ask your provider when considering a birth control implant.
What Is A Contraceptive Implant?
A contraceptive implant is a small, flexible rod that is inserted under the skin of the upper arm. It is about the size of a matchstick and contains a synthetic form of the hormone progestin. The implant measures 1.6 inches in length (4 centimeters) and is approximately 2 mm in diameter.
The only contraceptive implant available for use in the USA is called Nexplanon, which is approved by the FDA to prevent pregnancy for up to three years. Good, quality data shows that it is effective for up to five years, so while it is considered “off label” to use it for that long, it is reasonable to do so. It is a highly effective form of birth control, with a failure rate of less than 1%.
How Does It Work?
Contraceptive implants work by releasing a steady dose of progestin into the body. This hormone temporarily stops ovulation, which prevents the release of eggs from ovaries. It also thickens the cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach and fertilize an egg. In addition, it thins the lining of the uterus, which makes implantation of a fertilized egg more difficult.
The implant is inserted under the skin of the upper arm by a healthcare provider and can be easily removed at any time. It is a long-acting form of birth control, meaning that it does not require daily or monthly maintenance like other forms of birth control.
The implant does not contain estrogen or estradiol, so it is a good option for people who cannot take or wish to avoid estrogen.
Understanding Effectiveness
As mentioned earlier, contraceptive implants are one of the most effective forms of birth control available. Less than 1 out of 100 women or people assigned female at birth will become pregnant while using it each year. It is as effective as permanent birth control methods (vasectomy or getting tubes tied) but the contraceptive implant has the benefit of being reversible.
This high level of effectiveness is due to the fact that the implant does not rely on user compliance, unlike other forms of birth control such as the pill or condoms. Once inserted, the implant works continuously to prevent pregnancy.
Benefits
Contraceptive implants offer a range of benefits for women and people assigned female at birth, making them a popular choice for birth control. Some of the key benefits include:
Long-Lasting Protection
One of the main benefits of contraceptive implants is that they provide long-lasting protection against pregnancy. With a lifespan of up to five years, women and people assigned female at birth do not have to worry about daily or monthly maintenance, making it a convenient option for those with busy lifestyles.
Highly Effective
As mentioned earlier, contraceptive implants are some of the most effective ways of preventing pregnancy. They are over 99% effective.
Reversible
Unlike permanent forms of birth control such as a tubal ligation, contraceptive implants are reversible. They can be easily removed at any time, and fertility typically returns within a few weeks.
No Interference with Sex
Contraceptive implants do not interfere with sex in any way, making them a discreet and convenient option. There is no need to interrupt intimacy to use a contraceptive implant, unlike other forms of birth control, such as condoms.
Reduced Menstrual Cramps and Bleeding
Many people experience reduced menstrual cramps and bleeding while using contraceptive implants.
Potential Side Effects
While contraceptive implants are generally safe and well-tolerated, they may cause some side effects. These side effects may include:
Irregular Bleeding
Some women and people assigned female at birth may experience irregular bleeding while using contraceptive implants. This may include spotting, light bleeding, continuous bleeding, or no bleeding at all. This is a common side effect and is usually not harmful, but it may be bothersome for some people.
Headaches
Headaches are another potential side effect of contraceptive implants. These headaches may be mild or severe and may occur more frequently during the first few months of use.
Mood Changes
Hormonal changes caused by contraceptive implants may also lead to mood changes in some women and people assigned female at birth. This may include irritability, mood swings, or depression.
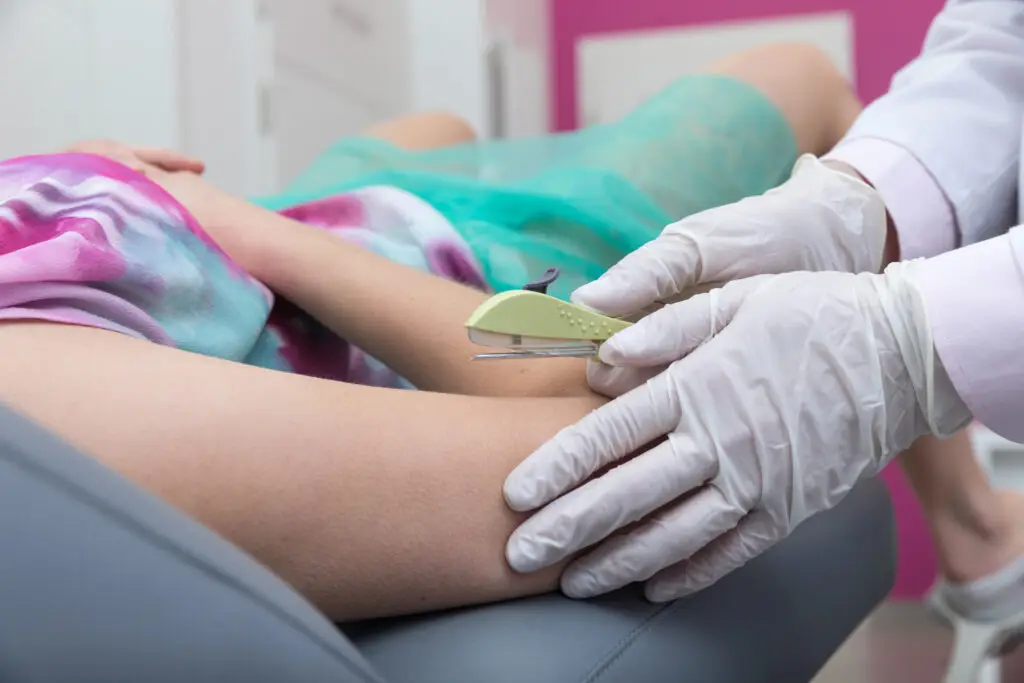
How to Get a Contraceptive Implant
If you are interested in getting a contraceptive implant, the first step is to schedule an appointment with us at Crossroads Medical Center. We will discuss your medical history and help you determine if a contraceptive implant is the right choice for you.
Once you have decided to get a contraceptive implant, the procedure is relatively simple and can be done in our office. The healthcare provider will numb the area on your upper arm and insert the implant under the skin. The procedure takes only a few minutes and typically causes very little pain.
Contraceptive implants are available at most local birth control clinics in Boulder, including here at Crossroads Medical Center. We specialize in providing a range of birth control options and can help you determine if a contraceptive implant is the right choice for you. Independently owned and operated, we take the time to listen to your needs and help you figure out the best birth control option for you, personally. Providing individualized and compassionate care is our priority.
Cost
The cost of a contraceptive implant can vary depending on your insurance coverage. However, most insurance plans cover the cost of contraceptive implants, making them an affordable option for many people.
Does The Contraceptive Implant Prevent STIs?
The contraceptive implant does not protect against Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs). Barrier methods, such as condoms and dental dams, are the best options for preventing STIs and they can be used in addition to the contraceptive implant.
Who Should Not Use A Contraceptive Implant?
A contraceptive implant is not recommended if you…
- Are pregnant
- Have, or have had blood clots, such as blood clots in your legs (deep vein thrombosis), lungs (pulmonary embolism), eyes (total or partial blindness), heart (heart attack), or brain (stroke)
- Have liver disease or a liver tumor
- Have unexplained vaginal bleeding
- Have breast cancer or any other cancer that is sensitive to progestin (a female hormone), now or in the past
- Are allergic to anything in NEXPLANON
Conclusion
The contraceptive implant is a highly effective form of birth control that offers a range of benefits for women and people assigned female at birth. It is a convenient, long-lasting option that does not require daily or monthly maintenance. If you are interested in getting a contraceptive implant, be sure to schedule an appointment with one of our healthcare providers to discuss your options and determine if it is the right choice for you.
